Q:You must hear the word VOCs very often. Do you really know that?
A: VOCs is the general term for volatile organic compounds discharged into the atmosphere by various human activities and biological metabolism, which can participate in the photochemical reaction of the atmosphere under the catalysis of nitrogen oxide to produce ozone. VOCs Is divided into anthropogenic source AVOCs and biological source BVOCs.
BVOCs
BVOCs (Biogenic Volatile Organic Cpmpounds) mainly comes from plants, and scientists have shown that the amount of plants emitting VOCs is about 10 times that of man-made VOCs emissions.
The vast majority of BVOCs in the atmosphere is placed into the atmosphere side by side through plant physiological processes, including isoprenoids, terpenes, alkanes, alcohols, alcohol, esters, carbon acyres and acids.
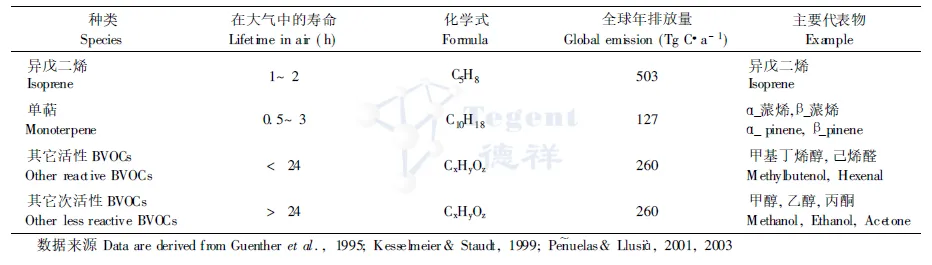
Table 1: Category [1] of biological source VOCs BVOCs
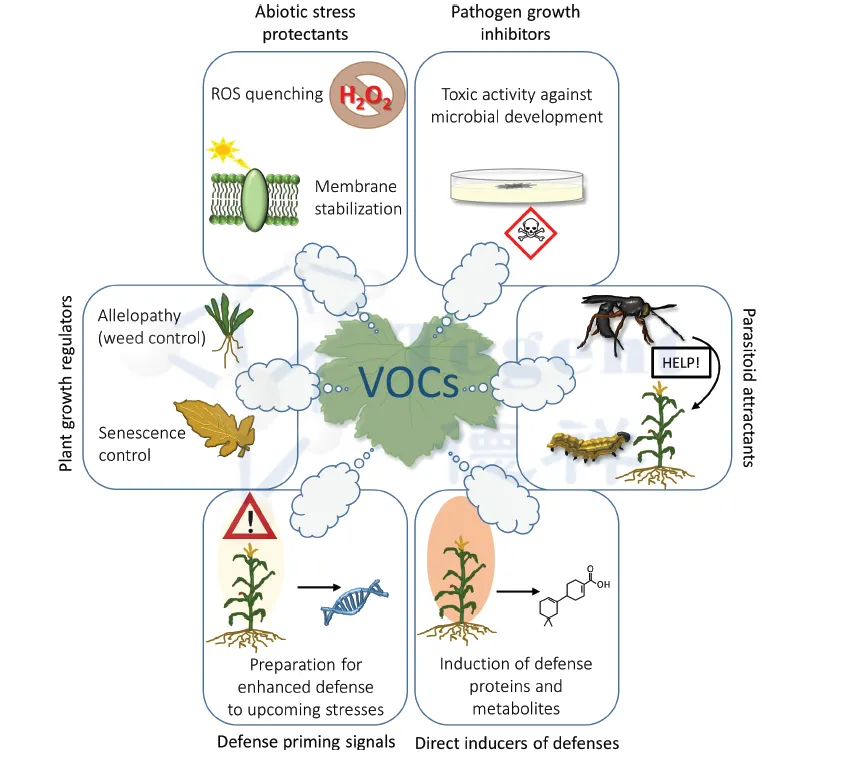
Analysis of volatile organic compounds released by plants still pays attention to the release of VOCs in agriculture, besides understanding the impact of VOCs on air pollution and global climate change.
Plants release VOCs is often a defense mechanism by releasing VOCs to attract natural enemies of herbivores, inhibiting the growth of plant pathogens in vitro or inducing plant antitoxins that can destroy the defense proteins and metabolites of pathogens, thus affecting the plant defense system; even some highly volatile VOCs can attract animals or insects to help pollination.
So, why is the BVOC so difficult to analyze?
1
Because the plant volatile organic compounds have very low content and high volatile characteristics, it is very difficult to extract enrichment, often need to collect a large number of 2-3L sample volume, or longer adsorption time to reach the detection limit of the instrument;
2
Analysis of plant VOC requires live sampling, which cannot be picked and heated! VOC composition before and after picking will change, so the plant can not be picked or sample processing, can be directly in living plants in situ sampling or direct field sampling;
3
The aroma composition of natural plants is complex, and it is recommended to use a wide range of adsorbent or coating for extraction analysis, to obtain a more complete compound map as possible.
Therefore, the establishment of highly sensitive and efficient analysis methods is the key to the qualitative and quantitative analysis of plant VOCs.
Q: So the question is, how to analyze the plant VOCs composition efficiently?
Analysis of the living plant VOCs
New extraction and analysis technology
Today, INNOTEG proposed a new extraction analysis technology ——Needle Trap that can analyze live plant VOCs, requiring only 100-300ml of volume to reach the detection limit of the common instrument GC-MS.
Needle Trap Dynamic needle capture technology
Needle Trap (NT) technology is a kind of active dynamic extraction method, its principle is to fill the adsorbent in the tip, by Sampling Case gas sample sample enrichment to the needle adsorbent, can by increasing the amount of adsorbent and composite different kinds of adsorbent in increasing adsorption capacity, suitable for a wider range of volatile organic compounds analysis.

Figure 1: NeedleTrap Dynamic capture pin
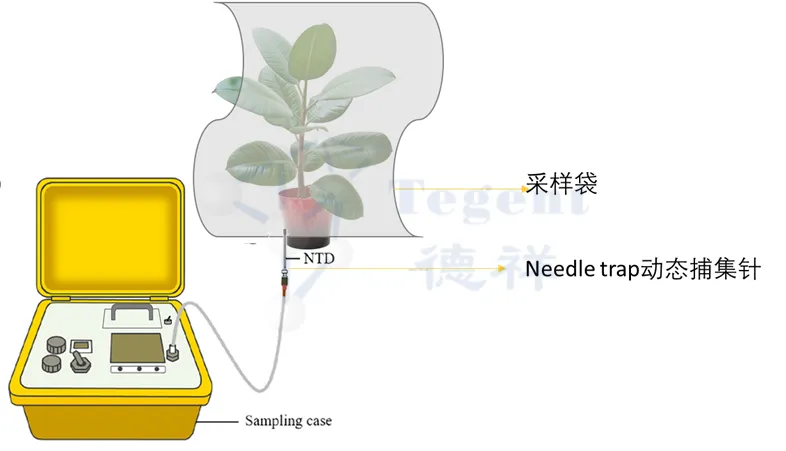
Figure 2: Simulation scheme of living plant sampling
Technical highlights:
● Active dynamic extraction, suitable for pptv-pbv level compound analysis, its high sensitivity;
● Even if the analysis of a very low concentration of plant VOC, only 100-300 mL samples are needed;
● Only 30s resolution time, fast gas phase thermal resolution, without the help of other thermal desorption equipment;
● WR filler compound Tenax TA, Carboxen1016, Carboxen1000 three kinds of adsorbent, can adsorb a wider range of compounds;
● Can be used for field sampling, set the sampling volume and sampling rate can be automatically sampling;
● Lithium battery charging design, convenient for the in-situ sampling of living plants.
Rll VOCs analysis cases
To gain insight into the types of compounds present in the headspace of living plants, we used SPME fibers and needles from INNOTEG and different Needle Trap to capture any volatile compounds that might be released from the plant.

Experiment
1. Direct sampling of live plants: 300ml were sampled from live plants and picked plants using Needle trap needles with different fillings, and 20min for SPME fibers;
2. The picked rings were brought to the laboratory and the degradation products were monitored 24 hours from the sampling date. Sample analysis was performed using an Agilent gas chromatograph (GC) coupled with an LECO mass spectrometer.
Conclusion
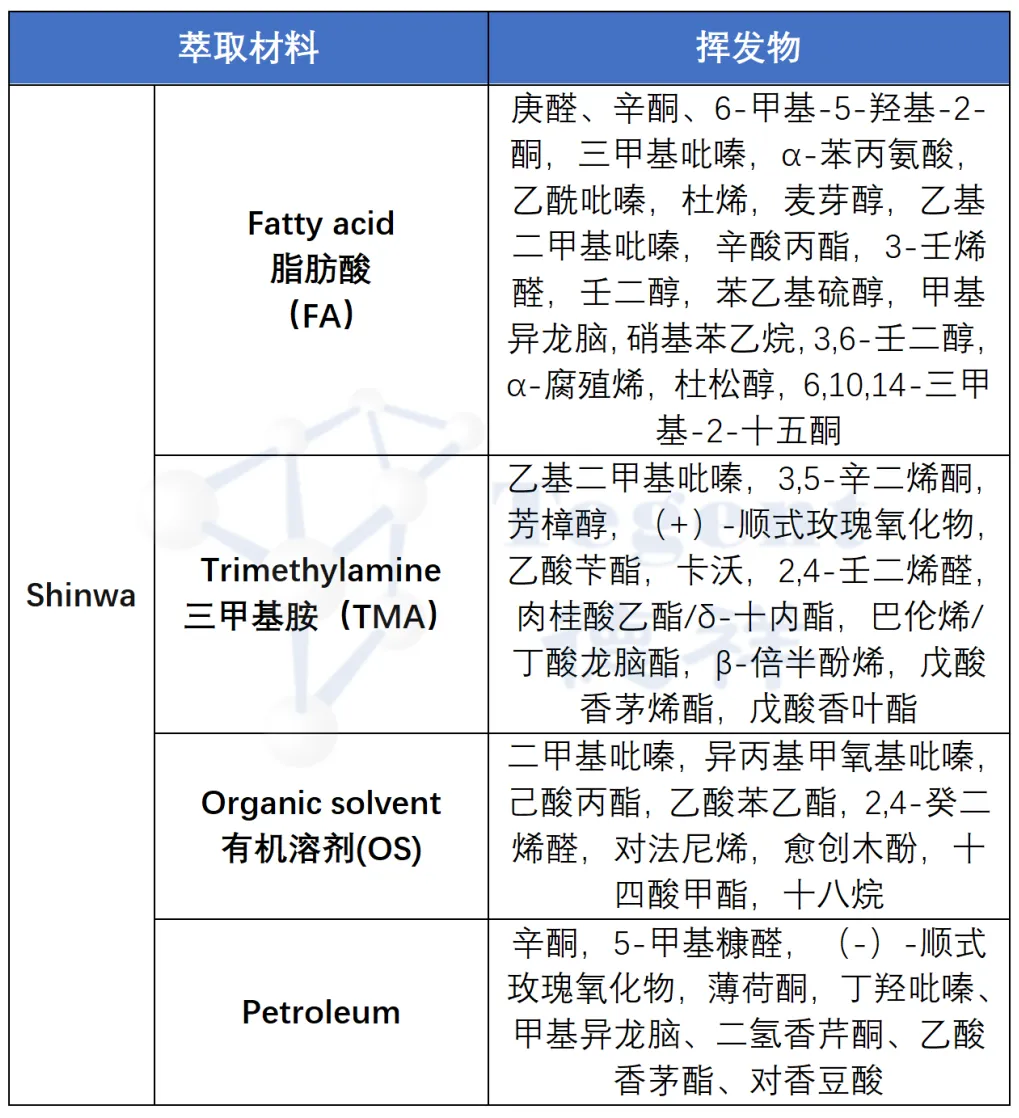
Table 2: Analysis results of Needle trap traps for different adsorbents
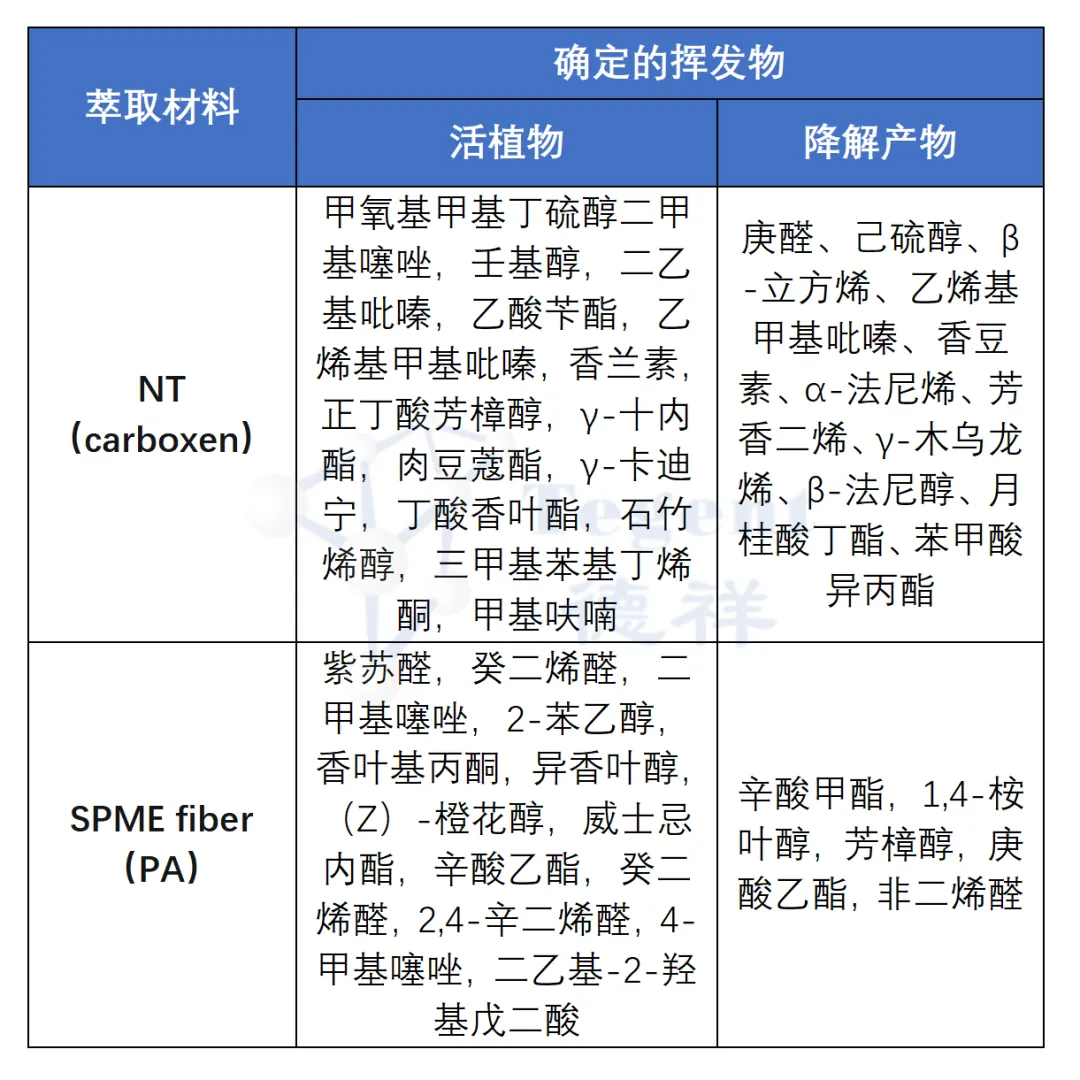
Table 3: Analysis of living plants and degradation products
Sum up
The results show that INNOTEG NeedleTrap (NT) dynamic needle capture technology provides a new and powerful sample preparation method for trace analysis in gaseous matrix. It can be used for in situ sampling of living subjects, with easy preservation and transportation after sampling.
INNOTEG Sampling Case (Gas sampler) The sampling flow rate of 1-50ml / min is adjustable, and the sampling amount is 0.1-10L. To meet the application needs of most volatile compounds in the industries such as flavor, spice, tobacco, Chinese herbal medicine research, plant protection, environmental pollution and so on.
Reference documentation:
[1] Wang Yongfeng, Li Qingjun, research progress in the emission and ecological function of VOCs in terrestrial ecosystems, Journal of Plant Ecology, 2005,29 (3): 487~ 496;
[2] Federico Brilli1*, Francesco Loreto2 and Ivan Baccelli1*.Exploiting Plant Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) in Agriculture to Improve Sustainable Defense Strategies and Productivity of Crops.doi: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00264
For purchase,please email:

18 Comment(s)
I love reading on 툰코 웹툰, so many amazing series!
1
1
Check out 뉴토끼 for free webtoons and great content.
1
1
안전놀이터 guarantees secure transactions.
1
1
I recommend 밤알바 직업소개소 to anyone who needs to work at night.
1
1
Find webtoons with deep characters and plots on 뉴토끼.
1
1
I appreciate how 북토끼 supports new creators with original content.
1
1
The user interface of 툰코 makes reading so easy.
1
1
If you’re a fan of webtoons, 블랙툰 is a must-visit!
1
1
Connecting with others on 뉴토끼 is so much fun!
1
1
Clean and comfortable rooms at 일산 노래방.
1
1
I’m impressed with the e-commerce features in 아임웹.
1
1
아임웹 makes managing my brand so much easier.
1
1
I love how customizable 아임웹's templates are!
1
1
아임웹 provides businesses with powerful analytics to make informed decisions.
1
Building a landing page with 아임웹 was so simple!
1
폰테크 is definitely changing how I shop for smartphones.
1
1
1
1
1
Leave a Comment